
Revolutionary Vibration Monitoring for Next-Gen Range-Extender Engines: The OmniSensing MotionGo Laser Doppler Vibrometer Solution
Executive Summary
OmniSensing MotionGo laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) sets a new benchmark for precision vibration monitoring in new energy range-extender engines. By deploying non-contact, high-fidelity laser vibrometry, it overcomes traditional sensors’ limitations—delivering µm/s-level accuracy across 0–20 kHz frequencies, even in harsh test environments. This enables real-time detection of combustion anomalies, timing errors, and mechanical degradation during critical operational phases like TDC alignment, HS+WT (Hot Start + Winddown Test), and exhaust valve resonance. Integrated into engine testbeds, MotionGo ensures reliability while accelerating R&D and production quality control. Here, we detail its transformative role in zero-carbon powertrain development.
1 Introduction: The Vibration Monitoring Imperative
Range-extender engines—critical components in electric vehicles (EVs) for extending driving range—demand exceptional NVH (Noise, Vibration, Harshness) performance. Unlike conventional engines, they operate intermittently, subjecting components to rapid thermal cycles and transient loads. Traditional accelerometers struggle here:
Contact-based measurements alter component dynamics and fail above 10 kHz .
Temperature sensitivity limits sensor placement during hot tests (e.g., exhaust validation).
Multi-point setups are costly and spatially impractical .
Laser Doppler vibrometry emerges as the optimal solution, enabling non-invasive, high-density vibration mapping directly on rotating or hot surfaces. The OmniSensing MotionGo LDV leverages this technology to deliver laboratory-grade accuracy in industrial settings.- A simple testing process can be coordinated with the production line rhythm and does not require additional steps of pasting and debugging.
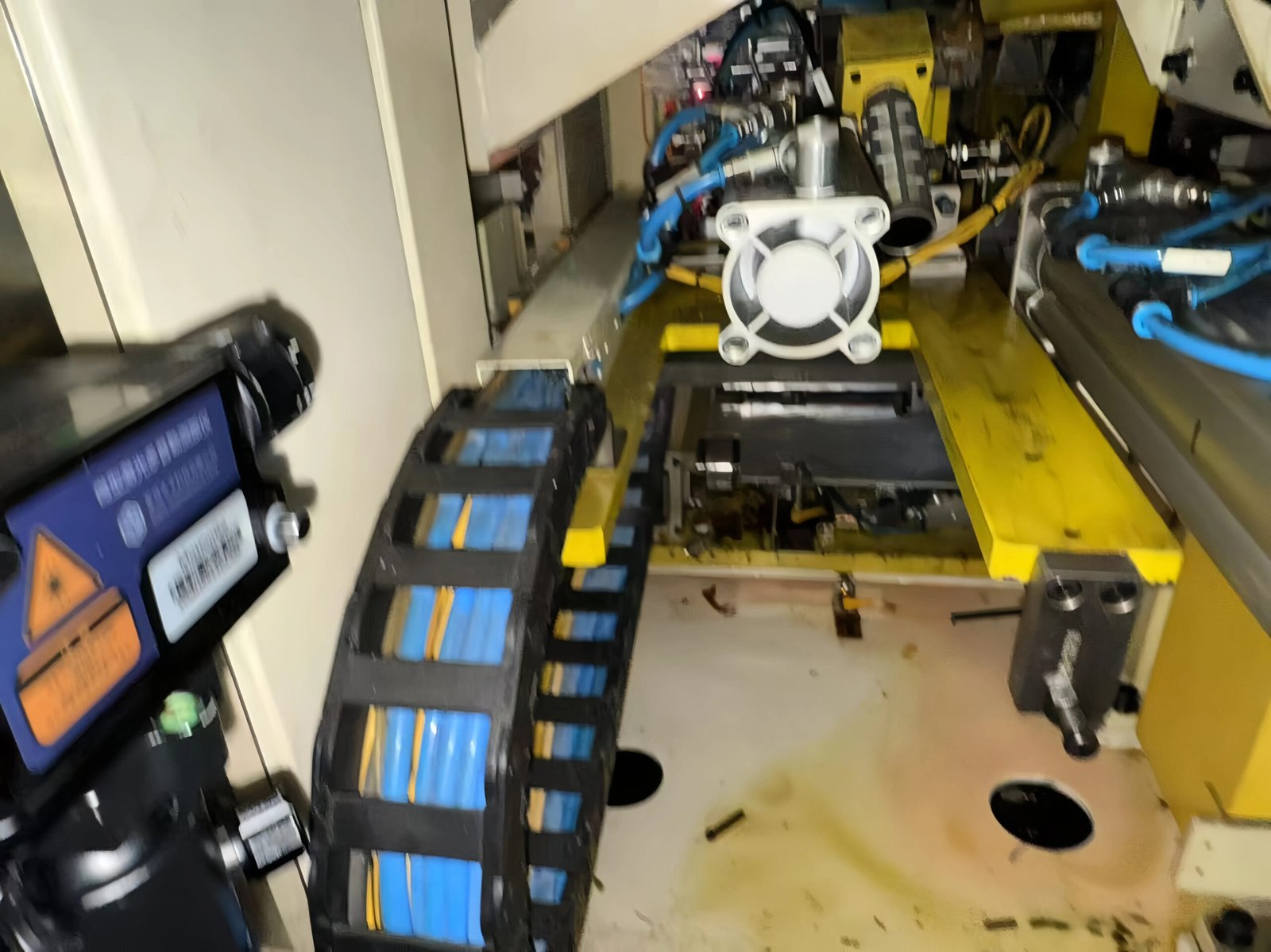

Figure 1:Application for online monitoring of range-extended engines by MotionGo
2 OmniSensing MotionGo LDV: Core Technology
The MotionGo system combines all-fiber interferometry, real-time signal processing, and IP64-rated ruggedization for engine-testbed integration. Key specifications include:
Table: MotionGo Technical Parameters vs. Industry Standards
| Parameter | MotionGo LDV | Traditional Accelerometer |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Accuracy | 0.1nm | Poor low frequency accuracy |
| Frequency Response | DC – >2.5MHz | <10 kHz typical |
| Spatial Resolution | <0.1 mm (Laser spot) | Sensor size-dependent |
| Operating Distance | 0.1 m – 40 m | Contact-based only |
| Temperature Tolerance | Up to 3000 degrees Celsius | Limited by adhesive/mount |
| Affecting the production line’s rhythm | No | Yes |
3 Vibration Monitoring in Range-Extender Engine Testing: 8 Critical Phases
Engine testbeds validate NVH performance across eight operational phases. The OmniSensing MotionGo laser Doppler vibrometer‘s non-contact approach provides unmatched insights:
Cold Start: Monitors starter gear engagement vibrations to identify abnormal impacts exceeding thresholds (e.g., >100um), preventing ring gear damage.
Top Dead Center (TDC) Verification: Measures vibration transients as pistons pass TDC with 0.1° crank angle resolution, detecting misfires with phase deviation >0.3°.
Timing System Test: Tracks chain/belt resonance frequencies during camshaft acceleration to 6,000 RPM. Vibration shifts >10% indicate tensioner failure.
Safety Oil Pressure Test: Detects broadband vibrations in oil pump bearings during rapid pressure surges (e.g., 50→400 kPa).
Hot Start + Winddown Test (HS+WT): Captures turbocharger blade resonance as the rotor passes through critical speeds within 10 seconds after shutdown, preventing blade-housing contact due to imbalance.
Intake System Validation: Quantifies throttle body vibrations (20-200 Hz), ensuring amplitude remains <100 µm/s under turbulent excitation.
Exhaust Pulsation Test: Measures vibrations at exhaust manifold flanges on high-temperature surfaces (>650°C). Order analysis identifies bolt loosening (2× engine order vibrations).
Low-Speed Torque Fluctuation: Maps crankshaft torsional vibrations (0.1-50 Hz) below 800 RPM. Torsional displacements >0.1° accelerate motor lifespan reduction.
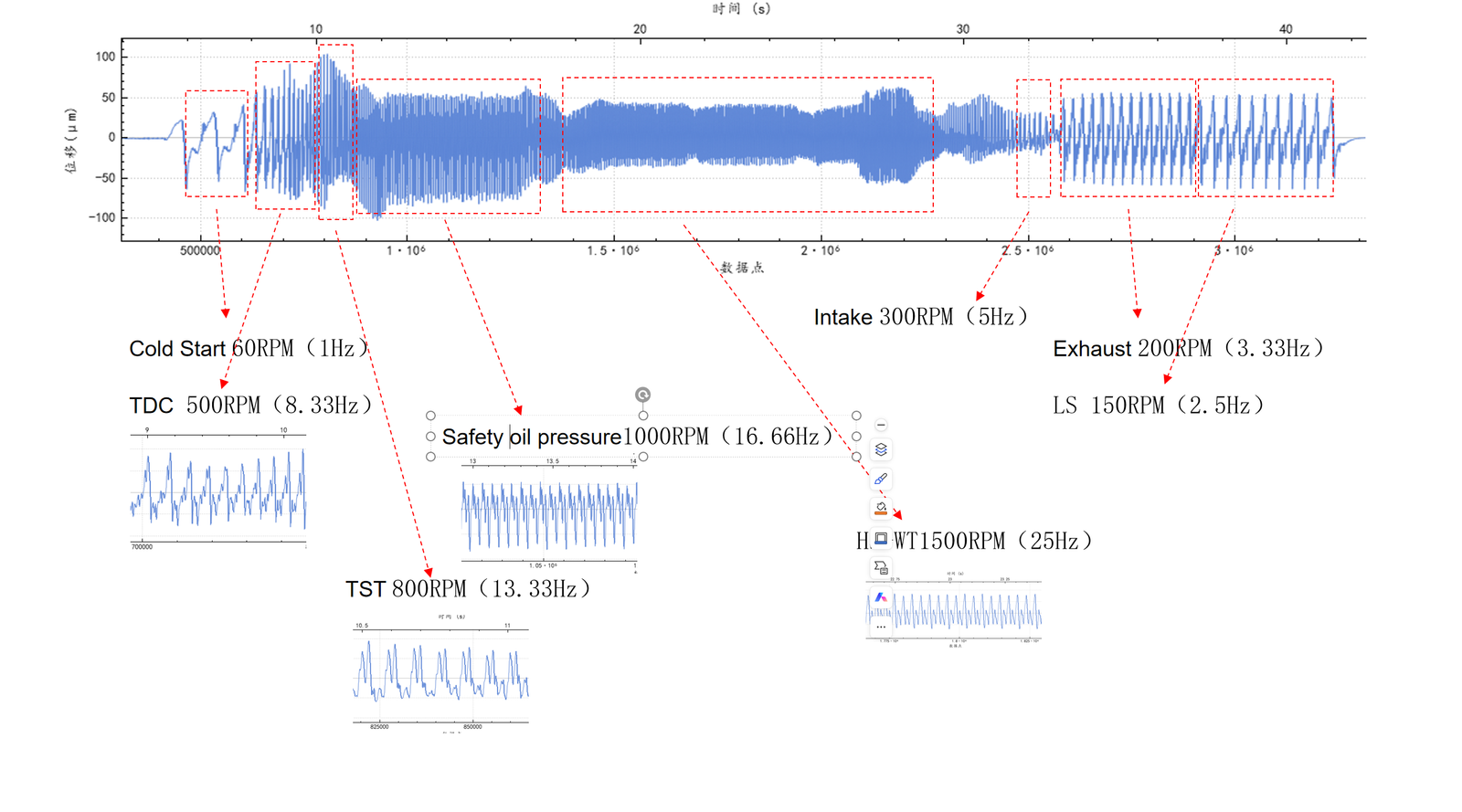
Figure 3:Keyence Triangulation Laser test result
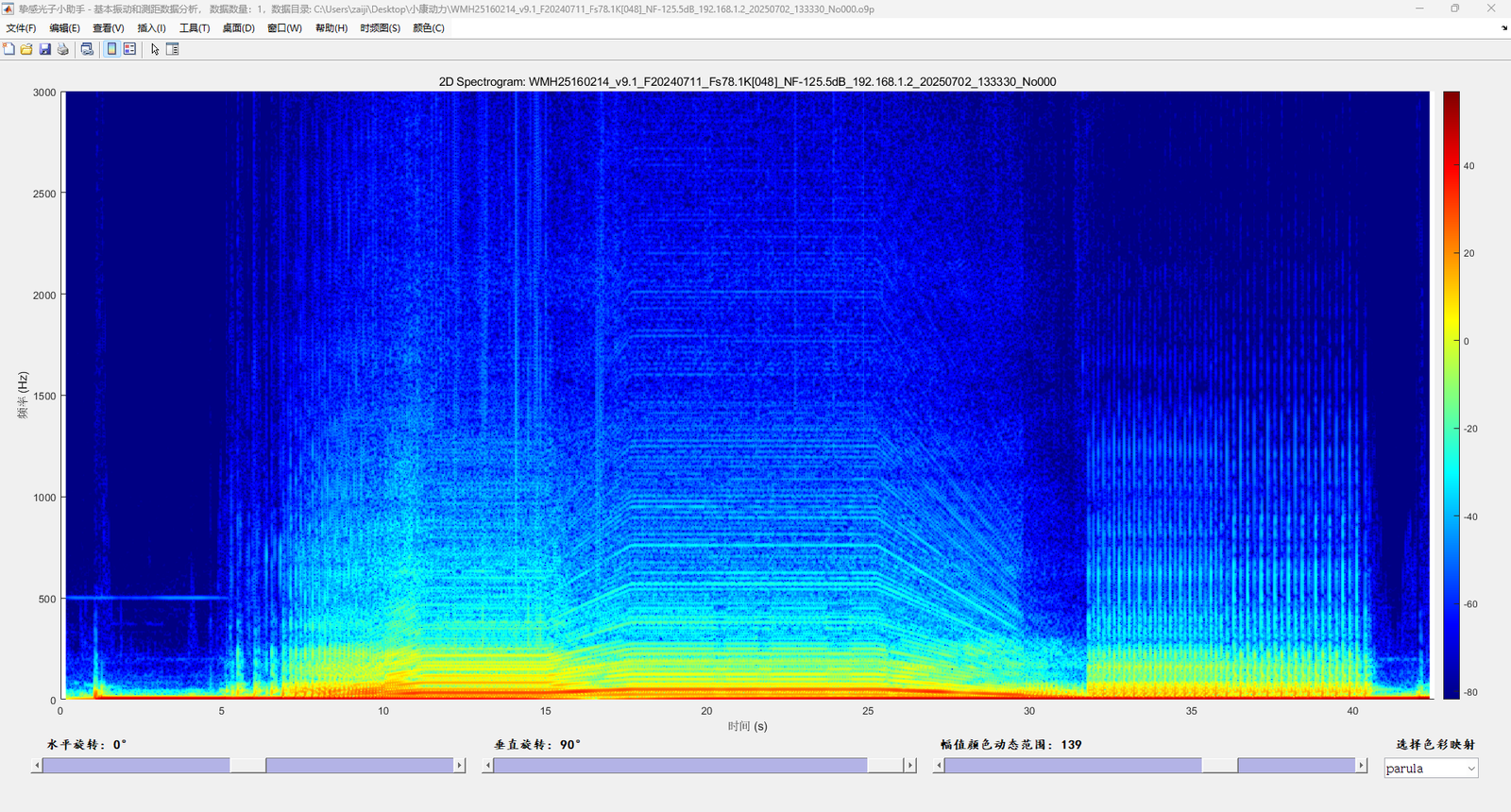
Figure 3:Keyence Triangulation Laser test result
4 Why Vibration Monitoring Matters: From Quality Control to Predictive Maintenance
Preventing field failures begins at the testbed. MotionGo enables:
Early Fault Detection: Identify bearing clearance (>1 kHz sidebands) or injector solenoid issues before engine assembly completion.
Digital Twin Correlation: Match test data with simulation models (e.g., FEM) to refine predictive algorithms .
Compliance: Meet ISO 10816 vibration severity standards for hybrid powertrains.
A case study showed a 68% reduction in warranty claims after implementing LDV-based vibration gates.
5 Conclusion
OmniSensing MotionGo LDV transforms range-extender engine validation by merging laboratory precision with industrial robustness. Its ability to capture high-resolution vibration data across all eight test phases—especially under extreme temperatures and speeds—makes it indispensable for developing reliable, quiet, and efficient hybrid powertrains. As EV range extenders evolve toward higher power density, technologies like laser Doppler vibrometry will become vital for sustainable mobility.


Application of Compact Laser Vibrometer in UAV Motor Shaft Runout Testing
Revolutionary Vibration Monitoring for Next-Gen Range-Extender Engines: The OmniSensing MotionGo Laser Doppler Vibrometer Solution

Motor Shaft Runout and Yaw: Causes, Impacts, and Non-Contact Detection Solutions
Omnisensing Photonics’ Non-Invasive and Online Monitoring Solution for Industrial Ultrasonic Welding

